You’ll find all the resources on Click2Engineering organized around 10 practices for developing an engineering mindset described by leading researchers in engineering education. These are practices used by engineers and are key to helping youth learn about engineering.
Engineers shape the world we live in and solve problems using systematic, iterative processes and a common set of engineering practices. These practices are also more fully described in educational research articles (Cunningham, 2018; Cunningham & Kelly, 2017).
High-quality engineering experiences that engage youth in these practices help youth understand how engineers approach their work and develop or strengthen an engineering mindset, or way of thinking.
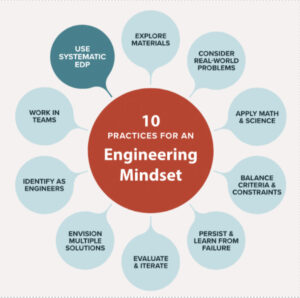
The 10 practices are:
- Use a systematic engineering design process
- Explore materials
- Consider real world problems
- Balance criteria and constraints
- Apply math and science
- Envision multiple solutions
- Evaluate designs and iterate
- Persist and learn from failure
- Work in teams
- Identify as engineers
Let’s look at each practice in a bit more detail. Engineers must balance all these practices in their work, but as youth are learning and developing their understanding, you may choose to emphasize some practices over others. You may also find different practices make sense to emphasize during different parts of an engineering experience. Don’t try to take on all the practices at the same time, just keep in mind the goal of learning to think and solve problems like an engineer.
Use a systematic engineering design process describes how engineers solve problems using a systematic, iterative process called the engineering design process. As they engage in authentic engineering experiences, youth should learn about the engineering design process and how to use it to develop innovative solutions. It is often easier to see this process in engineering experiences that you spend more time on. It may take several days for youth to experience the entire engineering design process and develop their own engineering solutions.
Explore materials describes how engineers consider the properties of materials as they select those that are most appropriate for their task. As they engage in authentic engineering experiences, youth should have opportunities to work with materials, consider their properties and select appropriate materials.
Consider real world problems describes how engineers design solutions to real-world problems in their work. They consider the context, background information, needs of the client, and the implication of possible solutions. Youth learning about engineering can also consider real world problems and should be encouraged to think about the context of the problem, the needs of the person, group or community impacted by the problem and how different solutions can have different implications.
Balance criteria and constraints describes how engineers, or youth learning about engineering, identify criteria and constraints using trade-offs to balance competing factors. Balancing criteria and constraints is a critical component of applying a systematic engineering design process and envisioning multiple solutions.
Apply math and science describes how engineers, or youth, use their knowledge of science, math, and other areas to solve problems they are facing. Even very young children have knowledge of math and science that they will use to solve problems.
Envision multiple solutions describes how engineers think innovatively to envision multiple possible solutions to open-ended problems. Authentic engineering experiences will present youth with challenges that do not have a single right answer. Youth will have to consider multiple solutions and make their own decision about what solution they think is best.
Evaluate designs and iterate describes how engineers, or youth learning about engineering, test their designs to see how well they work. They collect and analyze data to revise and improve solutions in an iterative process. Often, our initial ideas do not work when they are tested – that is where the next practice is needed.
Persist and learn from failure describes how engineers, or youth, learn from failure to revise and improve the designs. This requires perseverance and improving through multiple iterations. To develop this practice, it is critical that youth have time and resources so that can improve their solutions and learn from what went wrong.
Work in teams describes how engineers, or youth learning about engineering, must work together to bring a diversity of knowledge and perspectives to the problem. These are skills that are learned and improve with practice. Youth may need help learning to negotiate, communicate and work in teams. Engineering experiences can help develop these important life skills.
Identify as engineers describes how youth can begin to envision themselves as engineers when they are able to use these engineering practices and develop an engineering mindset. Helping youth learn about the diverse field of engineering, solve meaningful problems and meet role models that share their interests and background will help develop an engineering identity.
You’ll find resources on Click2Engineering to help you understand each of these practices, and how they come together to develop an engineering mindset. There are videos where you can see the practices in action and engineering experiences you can use to help youth develop the practices for an engineering mindset. While the resources on Click2Engineering were designed with out-of-school time educators in mind, they are flexible enough to be useful to anyone who needs help in developing their engineering education skills, be it someone who has no experience with engineering, or an engineer who would like to teach others.
